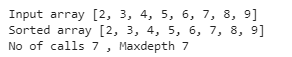Implementing Quicksort using Partition. Recursive and Iterative.
Quicksort and its optimization.
Continuing from our previous post at:
What you will learn in this post?
Implement Quicksort using Recursion.
Implement Quicksort using stack.
Analyze their Time Complexity.
Optimize the time complexity.
Let us revise the partitioning algorithm we implemented in the previous post.
So, we have learned how to partition an array, and this is the relevant code.
a=[5,6,4,9,8,2,3,7]
finalposition=0
pivot=a[0]
n=len(a)
for i in range(n):
if a[i]<pivot:
finalposition+=1
a[i],a[finalposition]=a[finalposition],a[i]
a[0],a[finalposition]=a[finalposition],a[0]
print(a)Output
We, are partitioning the array starting from left index=0 and ending at right index = length-1=7. We take as pivot the element at position 0.
The basic concept is to keep partitioning till all the partitions are reduced to one or less.
Here is the complete program with its output.
def quickSort(a,left,right):
if left>=right:
return
pivot=a[left]
finalposition=left
for i in range(left+1,right+1):
if a[i]>=pivot:
continue
finalposition+=1
a[i],a[finalposition]=a[finalposition],a[i]
a[left],a[finalposition]=a[finalposition],a[left]
quickSort(a,left,finalposition-1)
quickSort(a,finalposition+1,right)
a=[5,6,4,9,8,2,3,7]
print("Input array",a)
quickSort(a,0,len(a)-1)
print("Sorted array",a)Output
How do we find the depth of recursion and the total number of calls?
Look this up.
class ExecutionDetails:
noofcalls=0
maxdepthofrecursion=0
level=0
def quickSort(a,left,right,exdetails):
exdetails.level+=1
exdetails.noofcalls+=1
if exdetails.level>exdetails.maxdepthofrecursion:
exdetails.maxdepthofrecursion=exdetails.level
if left>=right:
exdetails.level-=1
return
pivot=a[left]
finalposition=left
for i in range(left+1,right+1):
if a[i]>=pivot:
continue
finalposition+=1
a[i],a[finalposition]=a[finalposition],a[i]
a[left],a[finalposition]=a[finalposition],a[left]
quickSort(a,left,finalposition-1,exdetails)
quickSort(a,finalposition+1,right,exdetails)
exdetails.level-=1
exdetails=ExecutionDetails()
a=[5,6,4,9,8,2,3,7]
print("Input array",a)
quickSort(a,0,len(a)-1,exdetails)
print("Sorted array",a)
print("No of calls",exdetails.noofcalls,", Maxdepth",exdetails.maxdepthofrecursion)Output
How, to reduce it. Check the size before calling the function.
Here is the updated code.
class ExecutionDetails:
noofcalls=0
maxdepthofrecursion=0
level=0
def quickSort(a,left,right,exdetails):
exdetails.level+=1
exdetails.noofcalls+=1
if exdetails.level>exdetails.maxdepthofrecursion:
exdetails.maxdepthofrecursion=exdetails.level
if left>=right:
exdetails.level-=1
return
pivot=a[left]
finalposition=left
for i in range(left+1,right+1):
if a[i]>=pivot:
continue
finalposition+=1
a[i],a[finalposition]=a[finalposition],a[i]
a[left],a[finalposition]=a[finalposition],a[left]
leftwidth=finalposition-left-1
rightwidth=right-finalposition-1
if leftwidth>=1:
quickSort(a,left,finalposition-1,exdetails)
if rightwidth>=1:
quickSort(a,finalposition+1,right,exdetails)
exdetails.level-=1
exdetails=ExecutionDetails()
a=[5,6,4,9,8,2,3,7]
print("Input array",a)
quickSort(a,0,len(a)-1,exdetails)
print("Sorted array",a)
print("No of calls",exdetails.noofcalls,", Maxdepth",exdetails.maxdepthofrecursion)Output
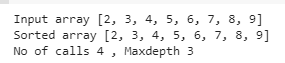
We have reduced the no of calls from 9 to 4 and maxdepth from 4 to 3.
What happens if we give a sorted array as input
class ExecutionDetails:
noofcalls=0
maxdepthofrecursion=0
level=0
def quickSort(a,left,right,exdetails):
exdetails.level+=1
exdetails.noofcalls+=1
if exdetails.level>exdetails.maxdepthofrecursion:
exdetails.maxdepthofrecursion=exdetails.level
if left>=right:
exdetails.level-=1
return
pivot=a[left]
finalposition=left
for i in range(left+1,right+1):
if a[i]>=pivot:
continue
finalposition+=1
a[i],a[finalposition]=a[finalposition],a[i]
a[left],a[finalposition]=a[finalposition],a[left]
leftwidth=finalposition-left-1
rightwidth=right-finalposition-1
if leftwidth>=1:
quickSort(a,left,finalposition-1,exdetails)
if rightwidth>=1:
quickSort(a,finalposition+1,right,exdetails)
exdetails.level-=1
exdetails=ExecutionDetails()
a=[2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
print("Input array",a)
quickSort(a,0,len(a)-1,exdetails)
print("Sorted array",a)
print("No of calls",exdetails.noofcalls,", Maxdepth",exdetails.maxdepthofrecursion)Output
The max depth increases because on one side we will always be getting a 1 sized array. Let us always set the middle number as pivot.
Make this change and we are back where we started.
class ExecutionDetails:
noofcalls=0
maxdepthofrecursion=0
level=0
def quickSort(a,left,right,exdetails):
exdetails.level+=1
exdetails.noofcalls+=1
if exdetails.level>exdetails.maxdepthofrecursion:
exdetails.maxdepthofrecursion=exdetails.level
if left>=right:
exdetails.level-=1
return
a[left],a[(left+right)//2]=a[(left+right)//2],a[left]
pivot=a[left]
finalposition=left
for i in range(left+1,right+1):
if a[i]>=pivot:
continue
finalposition+=1
a[i],a[finalposition]=a[finalposition],a[i]
a[left],a[finalposition]=a[finalposition],a[left]
leftwidth=finalposition-left-1
rightwidth=right-finalposition-1
if leftwidth>=1:
quickSort(a,left,finalposition-1,exdetails)
if rightwidth>=1:
quickSort(a,finalposition+1,right,exdetails)
exdetails.level-=1
exdetails=ExecutionDetails()
a=[2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
print("Input array",a)
quickSort(a,0,len(a)-1,exdetails)
print("Sorted array",a)
print("No of calls",exdetails.noofcalls,", Maxdepth",exdetails.maxdepthofrecursion)Output
We are back where we started.
One last optimization. Pick the smaller sized partition first.
The final optimized code.
class ExecutionDetails:
noofcalls=0
maxdepthofrecursion=0
level=0
def quickSort(a,left,right,exdetails):
exdetails.level+=1
exdetails.noofcalls+=1
if exdetails.level>exdetails.maxdepthofrecursion:
exdetails.maxdepthofrecursion=exdetails.level
if left>=right:
exdetails.level-=1
return
a[left],a[(left+right)//2]=a[(left+right)//2],a[left]
pivot=a[left]
finalposition=left
for i in range(left+1,right+1):
if a[i]>=pivot:
continue
finalposition+=1
a[i],a[finalposition]=a[finalposition],a[i]
a[left],a[finalposition]=a[finalposition],a[left]
leftwidth=finalposition-left-1
rightwidth=right-finalposition-1
if leftwidth<=rightwidth:
if leftwidth>=1:
quickSort(a,left,finalposition-1,exdetails)
if rightwidth>=1:
quickSort(a,finalposition+1,right,exdetails)
else:
if rightwidth>=1:
quickSort(a,finalposition+1,right,exdetails)
if leftwidth>=1:
quickSort(a,left,finalposition-1,exdetails)
exdetails.level-=1
exdetails=ExecutionDetails()
a=[2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
print("Input array",a)
quickSort(a,0,len(a)-1,exdetails)
print("Sorted array",a)
print("No of calls",exdetails.noofcalls,", Maxdepth",exdetails.maxdepthofrecursion)Output
Quicksort using stack
class stack:
def __init__(self):
self.a = []
def isEmpty(self):
return len(self.a) <= 0
def push(self, x):
self.a.append(x)
def pop(self):
if self.isEmpty():
return None
return self.a.pop()
def __str__(self):
return str(self.a)
def quickSort(a):
left = 0
right = len(a) - 1
st = stack()
st.push((left, right))
while not st.isEmpty():
left, right = st.pop()
if left >= right:
continue
pivot = a[left]
finalposition = left
for i in range(left + 1, right + 1):
if a[i] >= pivot:
continue
finalposition += 1
a[i], a[finalposition] = a[finalposition], a[i]
a[left], a[finalposition] = a[finalposition], a[left]
st.push((left, finalposition - 1))
st.push((finalposition + 1, right))
a = [9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
print("Input array", a)
quickSort(a)
print("sorted array", a)
Output
Unoptimized as yet. Please optimize and post here in the comments.
Happy reading🙂.
The Colab code is at.
We will write code for detecting the best degree polynomial next week.